Expansion:
Gradient Recalled Acquisition in Steady State
Technique:
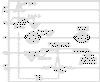
A series of sequential RF pulses is applied with a specific flip angle and interval TR. Three echoes result: an FID, SE, STE. In a GRASS sequence, the readout (frequency encode) gradient is extended to shift the SE and STE from the sampling window (to prevent FLASH bands). A rewinder gradient restores the original phase state (a necessity to maintain a steady state).
Typical Parameters:
optimal flip angle (Ernst angle) at a given TR
cos (angle) = exp (-TR/T1)
Short TR necessary to maintain steady state
Short TE increases signal to noise, decreases T2* weighting
Reference:
All You Really Need to Know About MR Physics, 7-6.
Contributor:
Related Sequences/Terms:
GRE, FISP, FAST, Steady State, STE
Comments:
To maintain steady state:
|
|||
| optimal flip angle at given TR is the Ernst angle |
Pulse Sequence Diagram: